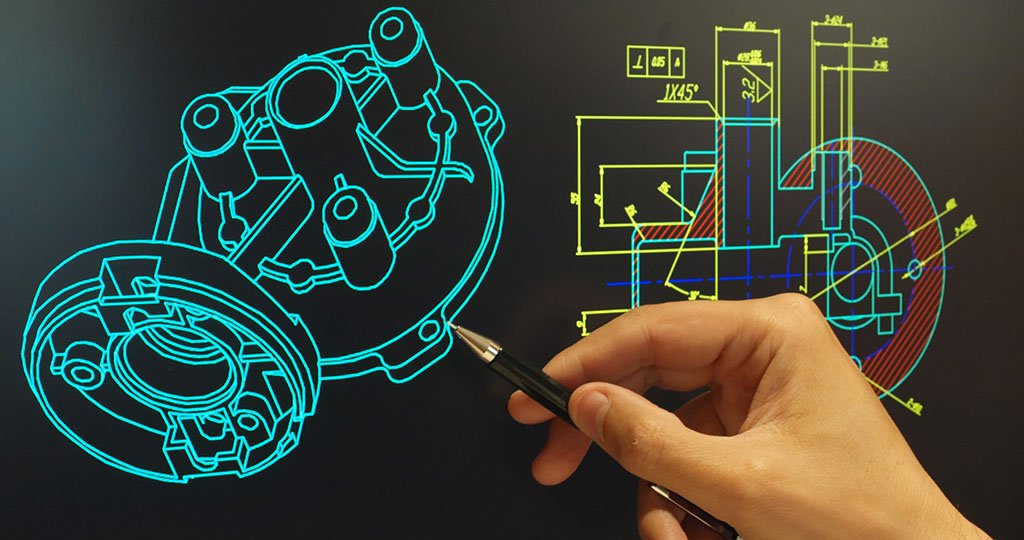
Introduction
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a technology that allows engineers, architects, and designers to create precise drawings, technical illustrations, and 3D models using computer software. It has completely transformed traditional manual drafting by introducing digital design accuracy, speed, and flexibility.
Definition
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design, which refers to the process of using computers and software tools to assist in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. It is widely used across industries such as mechanical engineering, civil construction, architecture, product design, and manufacturing.
Key Features of CAD Software
- 2D Drafting & 3D Modeling: Enables users to design everything from flat drawings to complex 3D objects.
- Precision and Accuracy: Exact dimensions, scaling, and geometric alignment reduce human errors.
- Simulation & Visualization: Designers can visualize how the product will look and perform before production.
- Automated Documentation: CAD software can automatically generate blueprints, assembly guides, and part lists.
- Design Revisions: Easy modification and iteration without redrawing from scratch.
Types of CAD
- 2D CAD – Used for flat drawings like floor plans, electrical schematics, and layouts.
- 3D CAD – Used for detailed product modeling, prototyping, and virtual simulations.
- Parametric CAD – Uses parameters and constraints for flexible, intelligent design changes.
- Freeform CAD – Focused on artistic, organic, and complex shapes for industrial or aesthetic design.
Benefits of Using CAD
- Enhanced Productivity: Faster design creation and easy modification.
- Improved Accuracy: Minimizes design errors and ensures dimensional consistency.
- Better Visualization: 3D renders and animations make designs easier to understand.
- Collaboration: Teams can work simultaneously on shared digital models.
- Cost Savings: Reduces waste, rework, and development time.
Applications of CAD
CAD is used across a variety of fields:
- Mechanical Engineering: Machine parts, assemblies, and tools.
- Architecture: Building layouts, elevations, and structural design.
- Civil Engineering: Infrastructure projects, roads, and bridges.
- Electrical Engineering: Circuit layouts and wiring diagrams.
- Product Design: Consumer goods, furniture, and industrial products.
Popular CAD Software
Some of the leading CAD tools include:
- AutoCAD
- SolidWorks
- CATIA
- Siemens NX
- Fusion 360
- SketchUp
- PTC Creo
- DraftSight
Conclusion
In the modern design world, CAD is not just a tool — it’s a necessity. It empowers professionals to visualize, test, and refine their ideas with unmatched accuracy and efficiency. Whether you are designing a small component or a large structure, CAD helps turn imagination into innovation.